|
 |
by Sabrina Oliveira, Mohamed Saifullah Hussin, Thomas Stützle, Andrea Roli and Marco Dorigo
Last updated in January 2017
| Submitted to IEEE CEC 2017 This page contains all supplementary information that, for the sake of conciseness, was not included in the paper. Table of Contents |
Keywords: Traveling salesman problem, quadratic assignment problem, ant colony optimization, population based ant colony optimization.
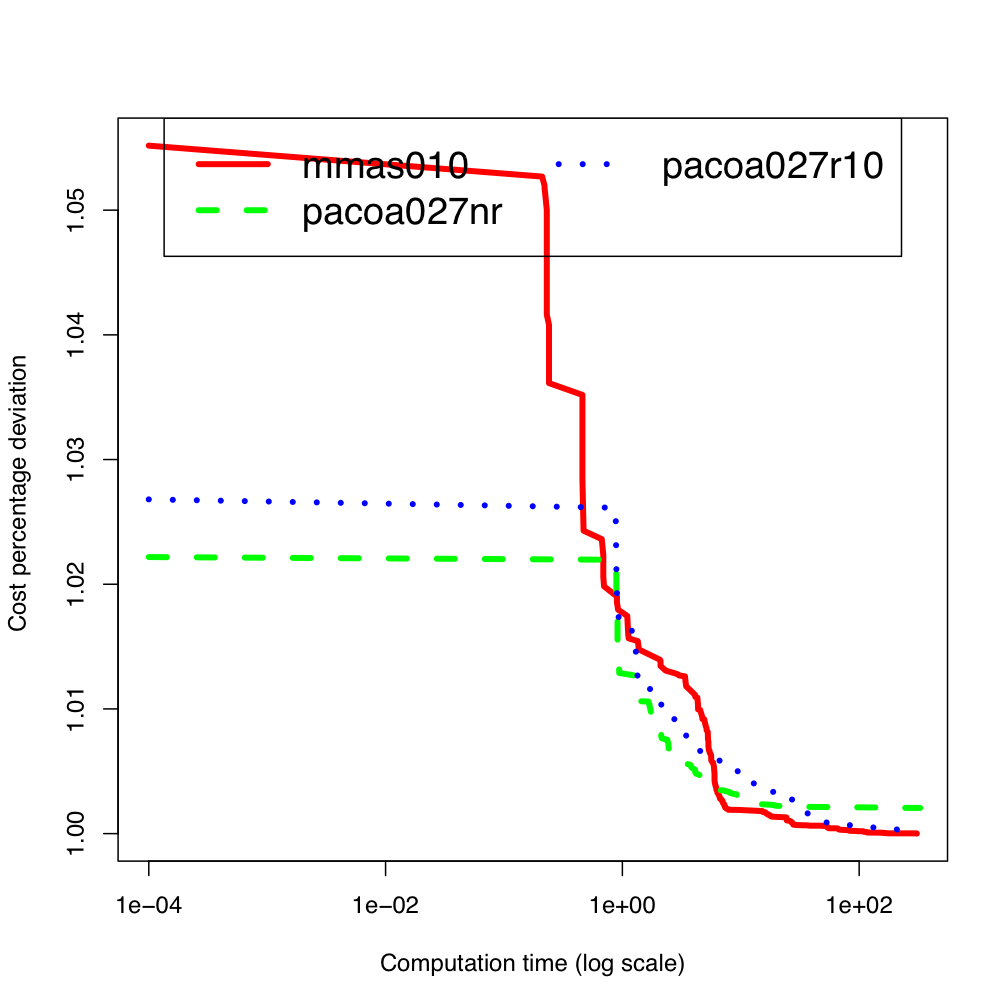
eil101
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
kroA200
 |
 |
rd400
 |
 |
d657
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
eil101
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
kroA200
 |
 |
kroA400
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
eil101
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
kroA200
 |
 |
rd400
 |
 |
d657
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
eil101
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
kroA200
 |
 |
rd400
 |
 |
d657
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
u2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
eil101
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
kroA200
 |
 |
rd400
 |
 |
d657
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
eil101
 |
 |
d198
 |
 |
kroA200
 |
 |
rd400
 |
 |
d657
 |
 |
u1817
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
u724
 |
 |
d2103
 |
 |
u2319
 |
 |
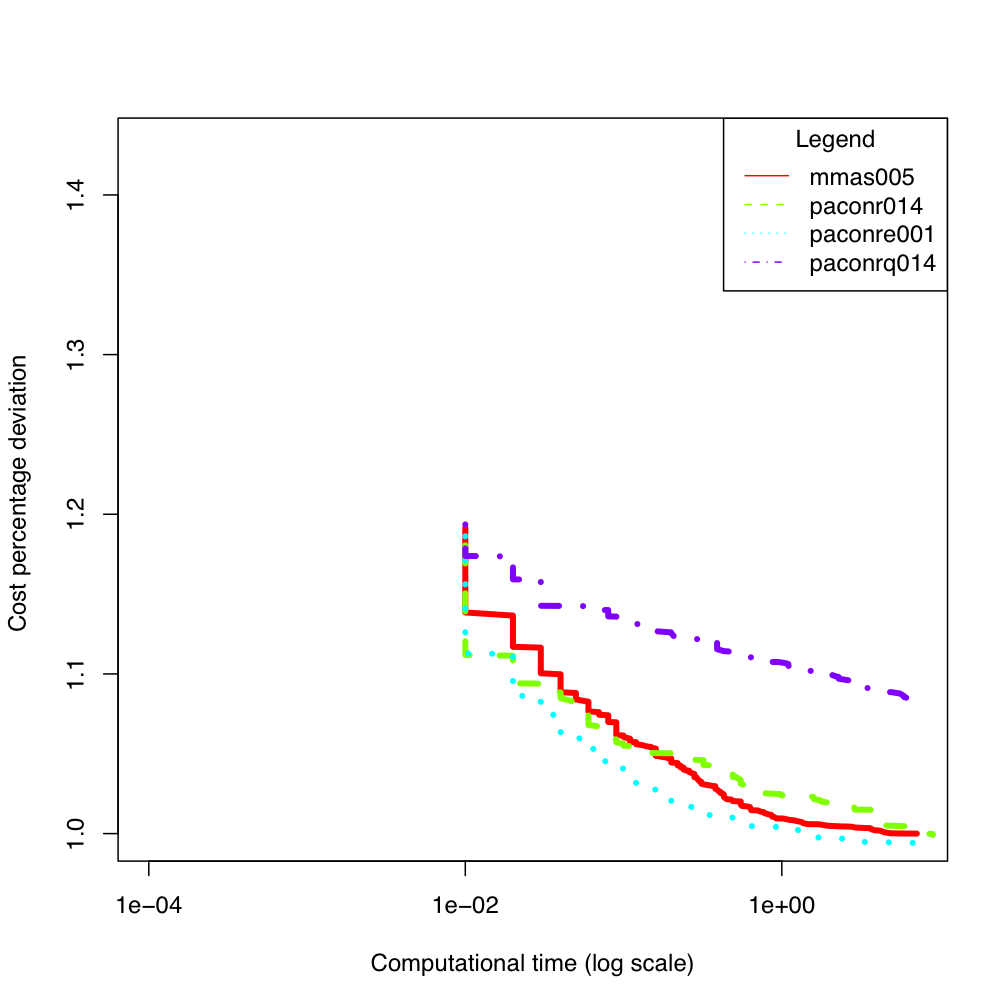 wil50
wil50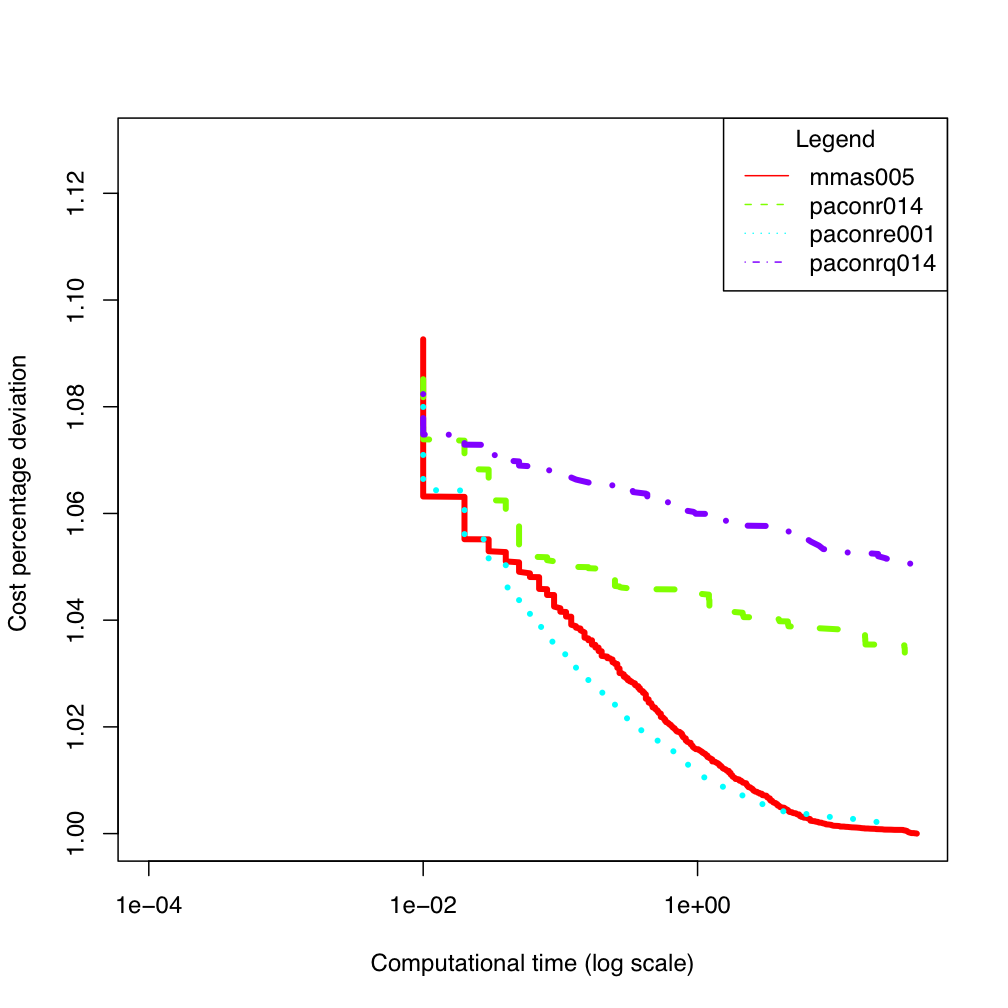
 tai100b
tai100b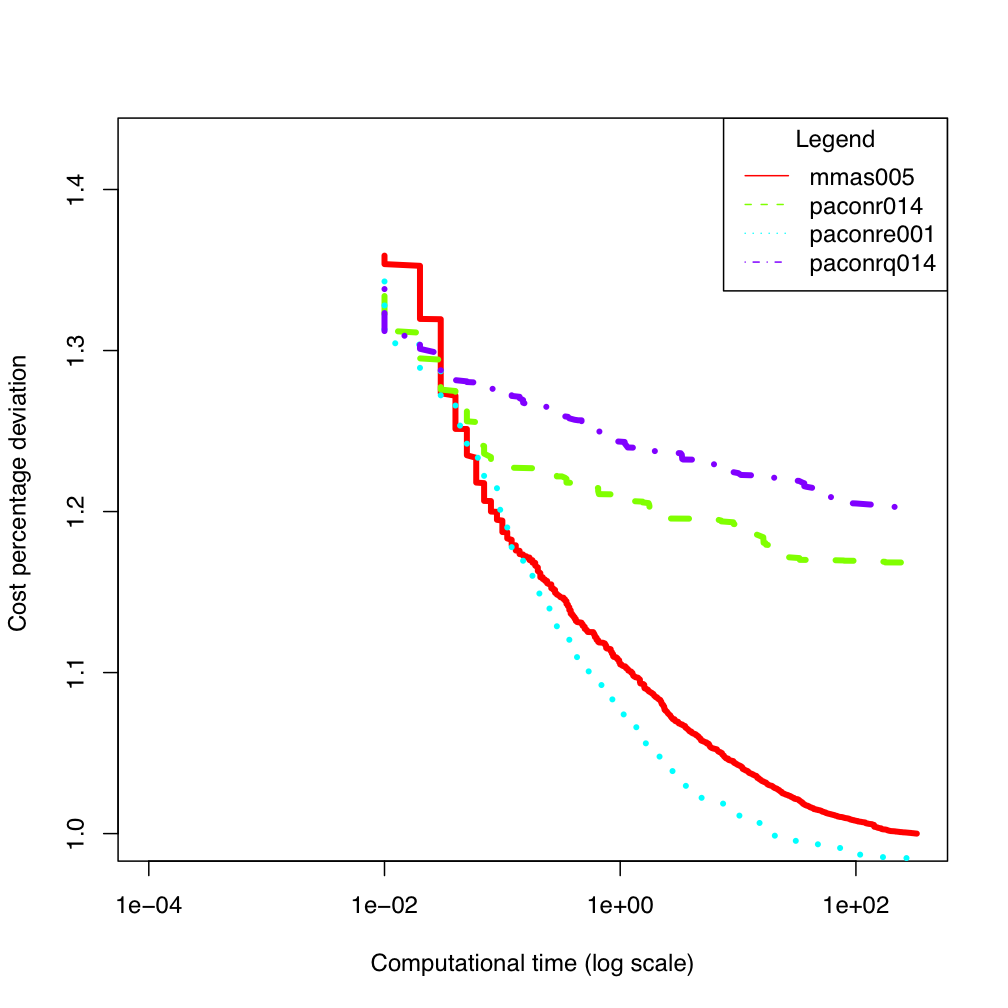 ES300
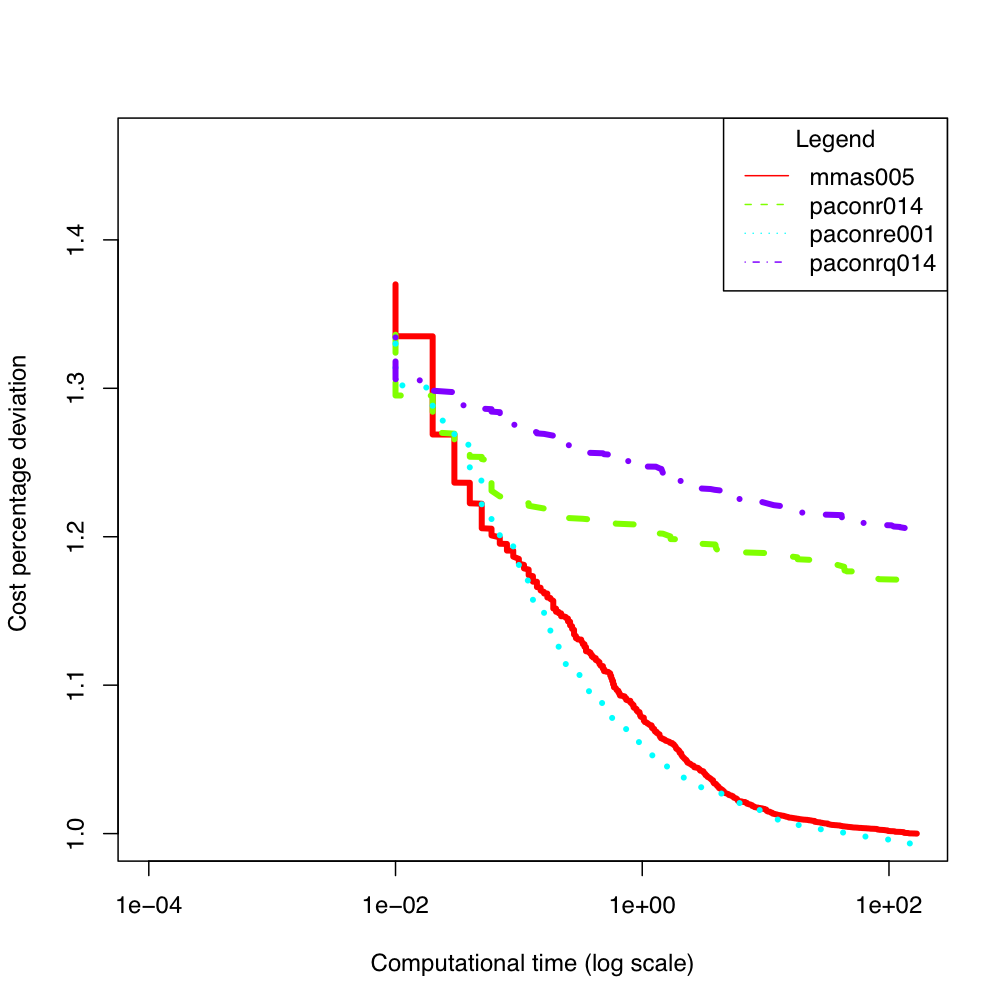
ES300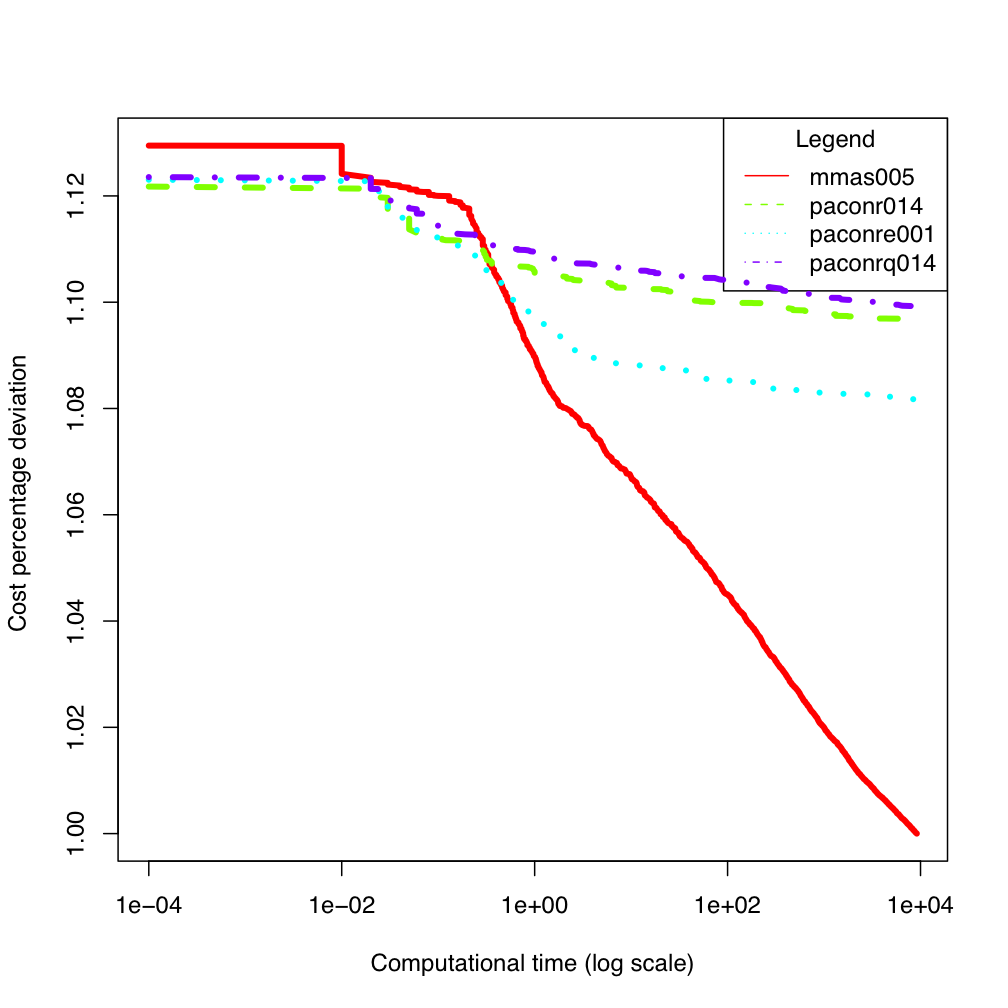
 wil50
wil50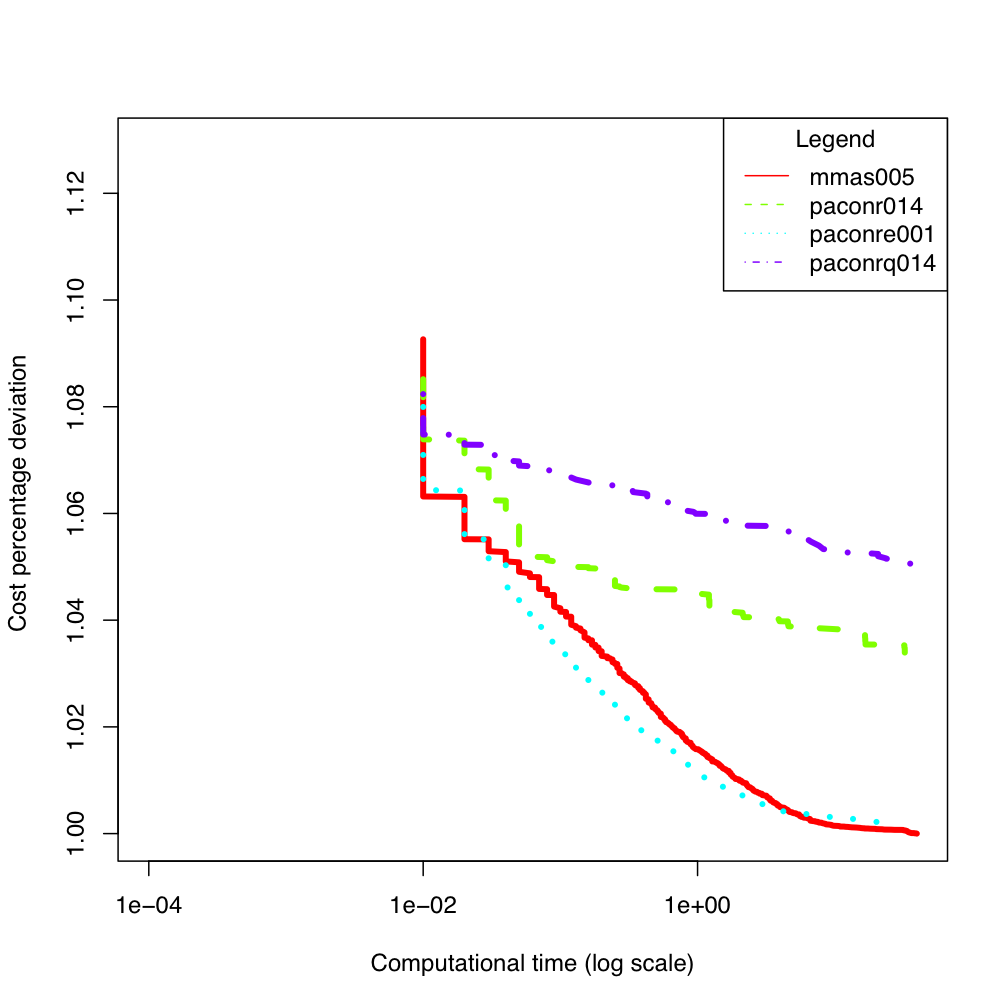 tai80b
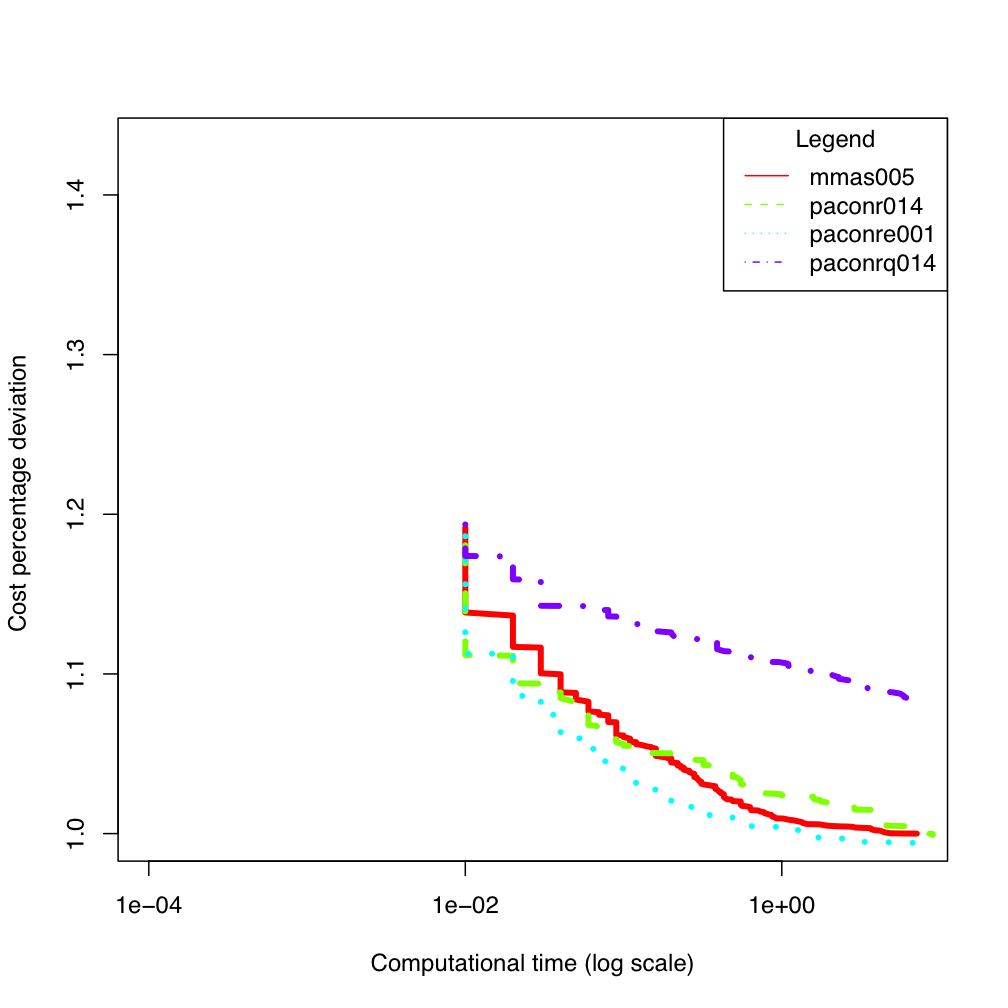
tai80b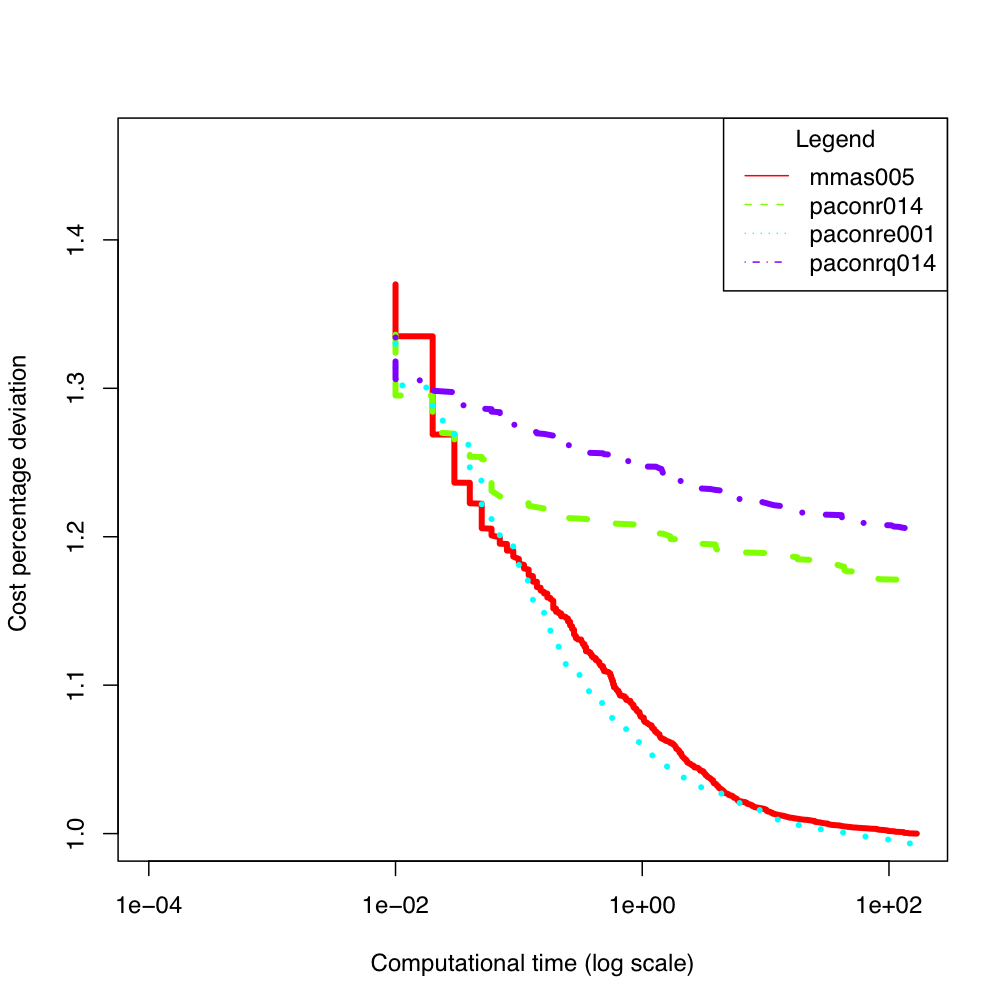 tai100b
tai100b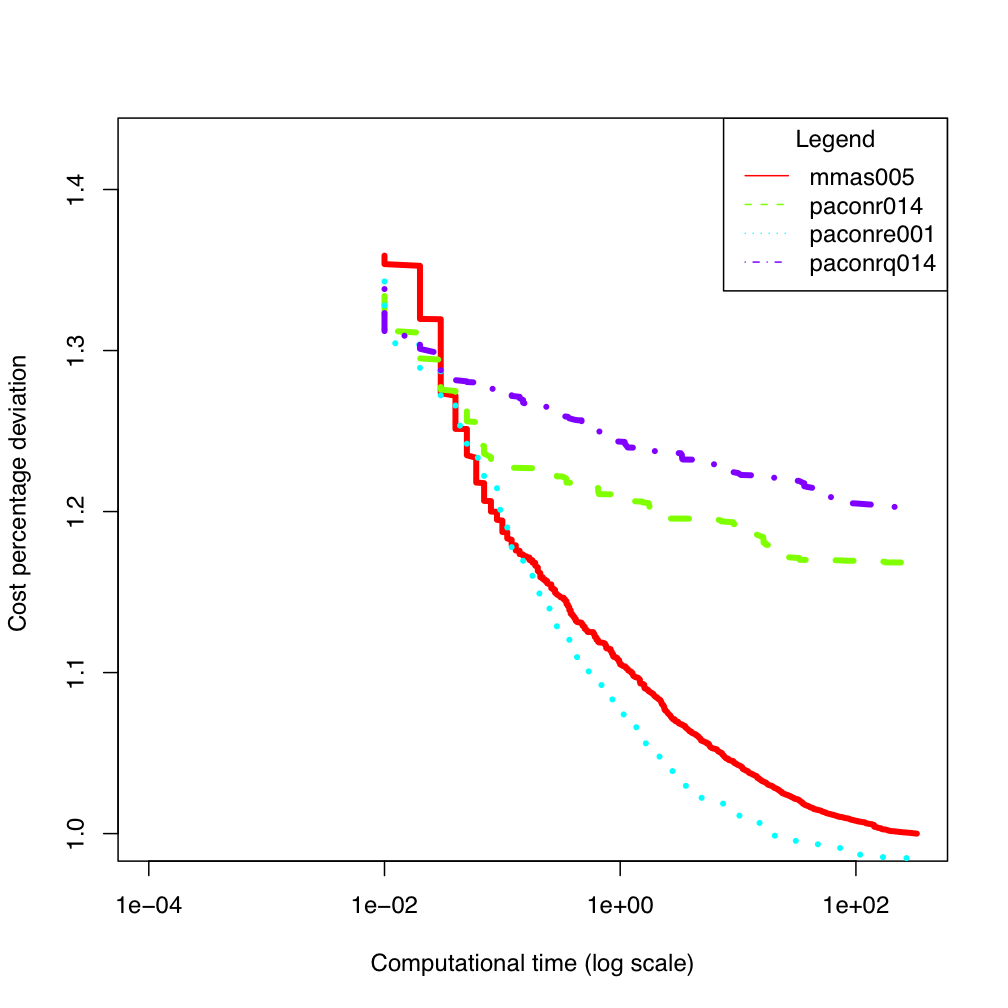 ES300
ES300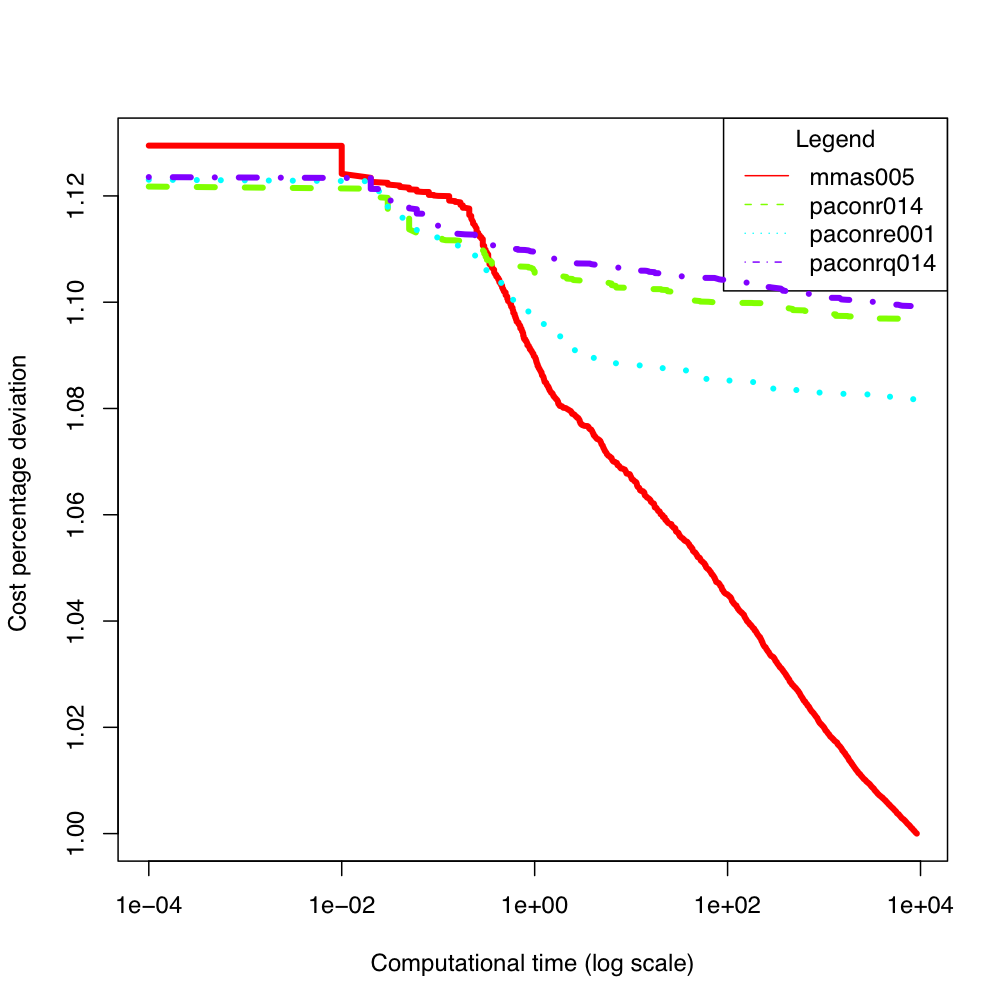
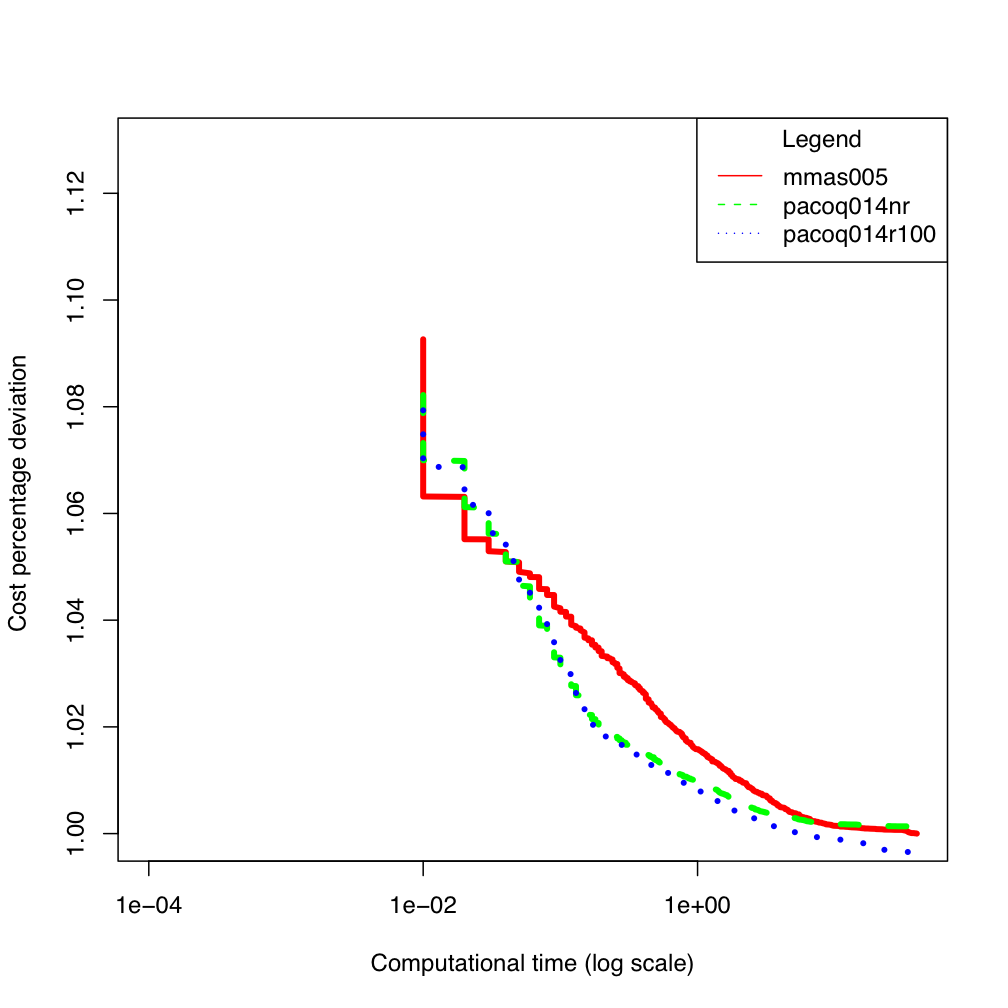 tai80b
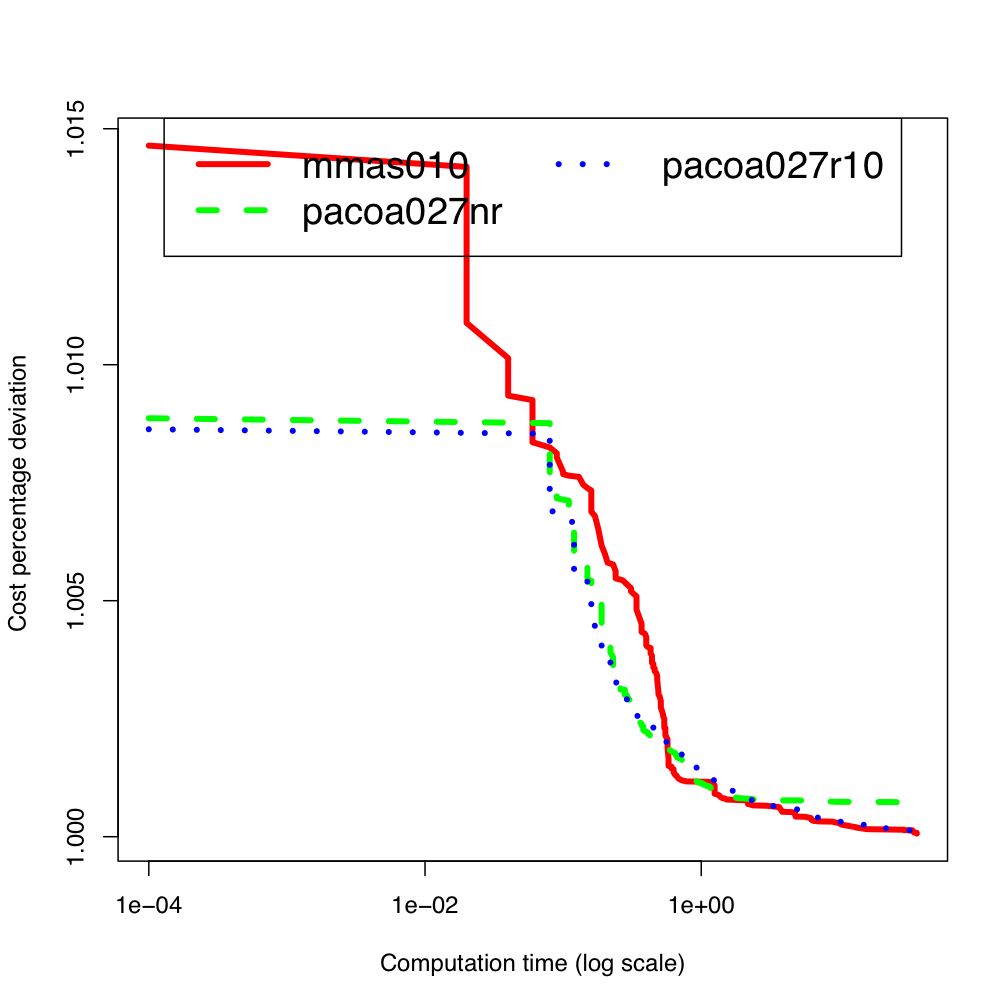
tai80b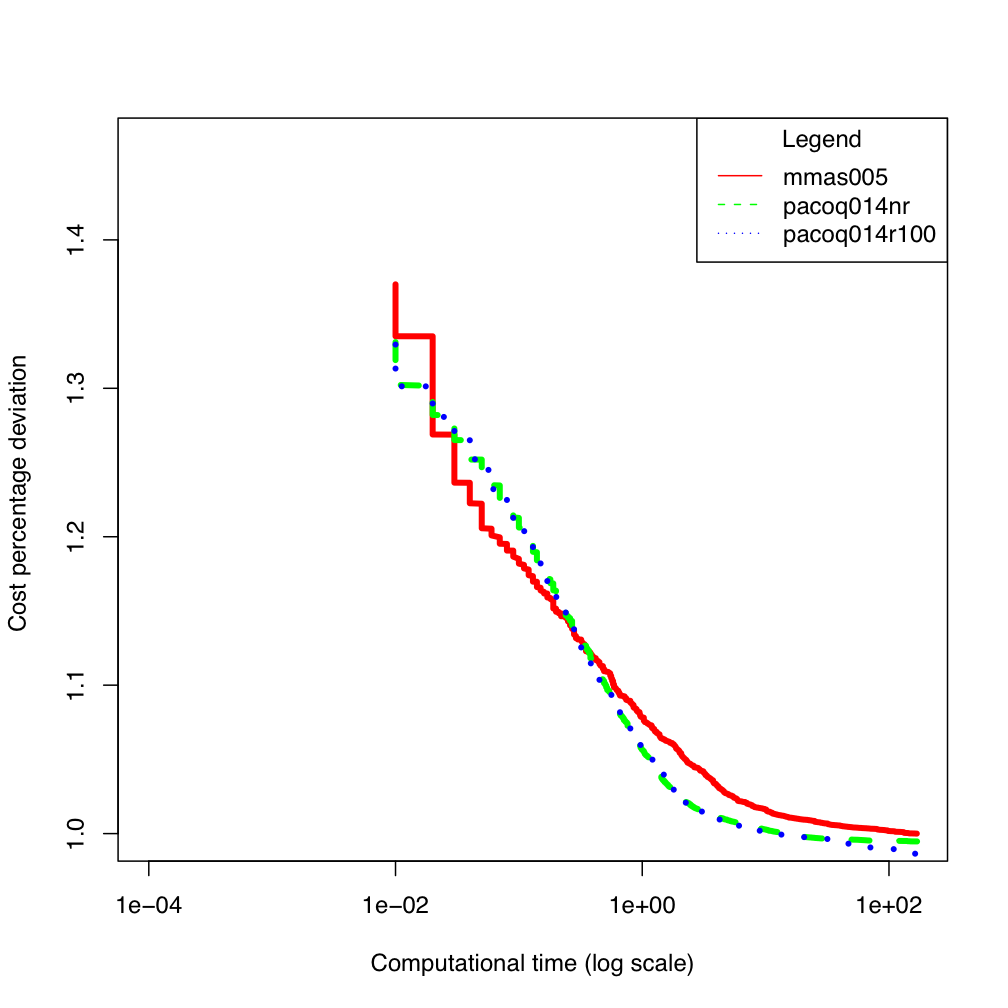 tai100b
tai100b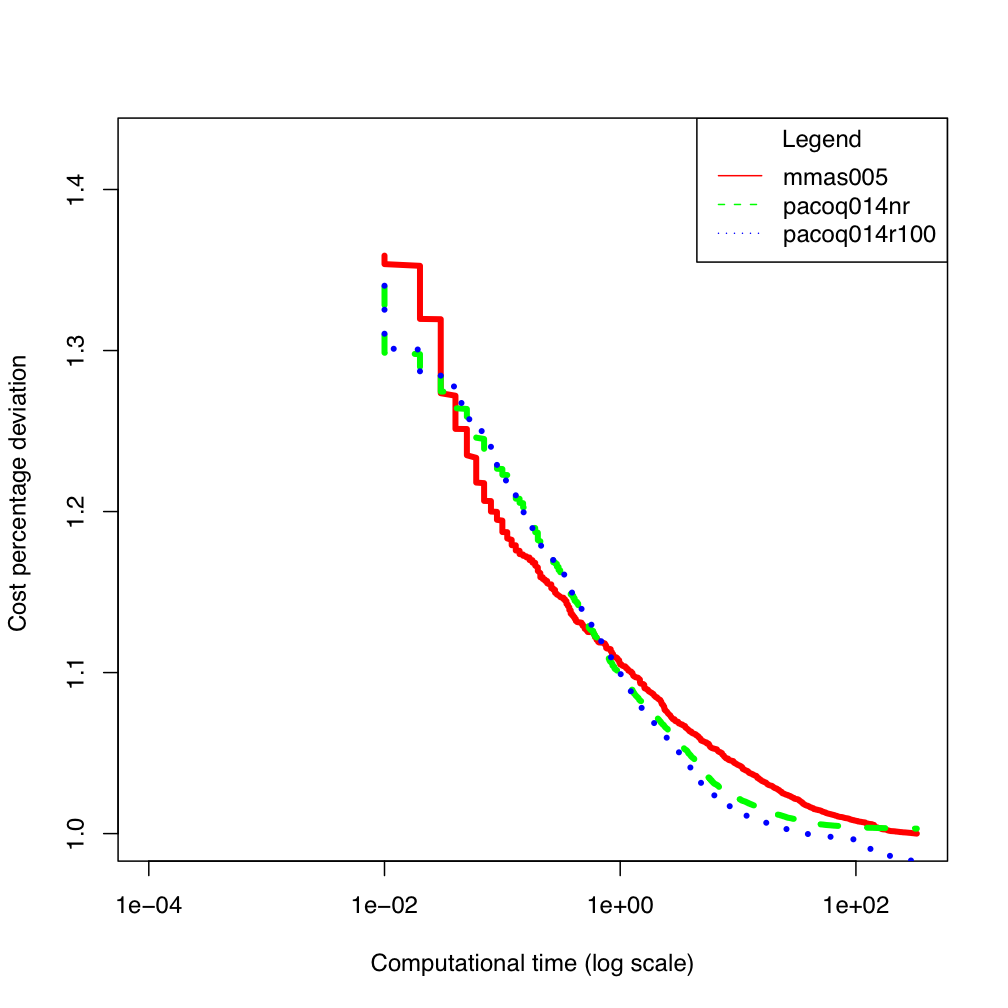
 tai80b
tai80b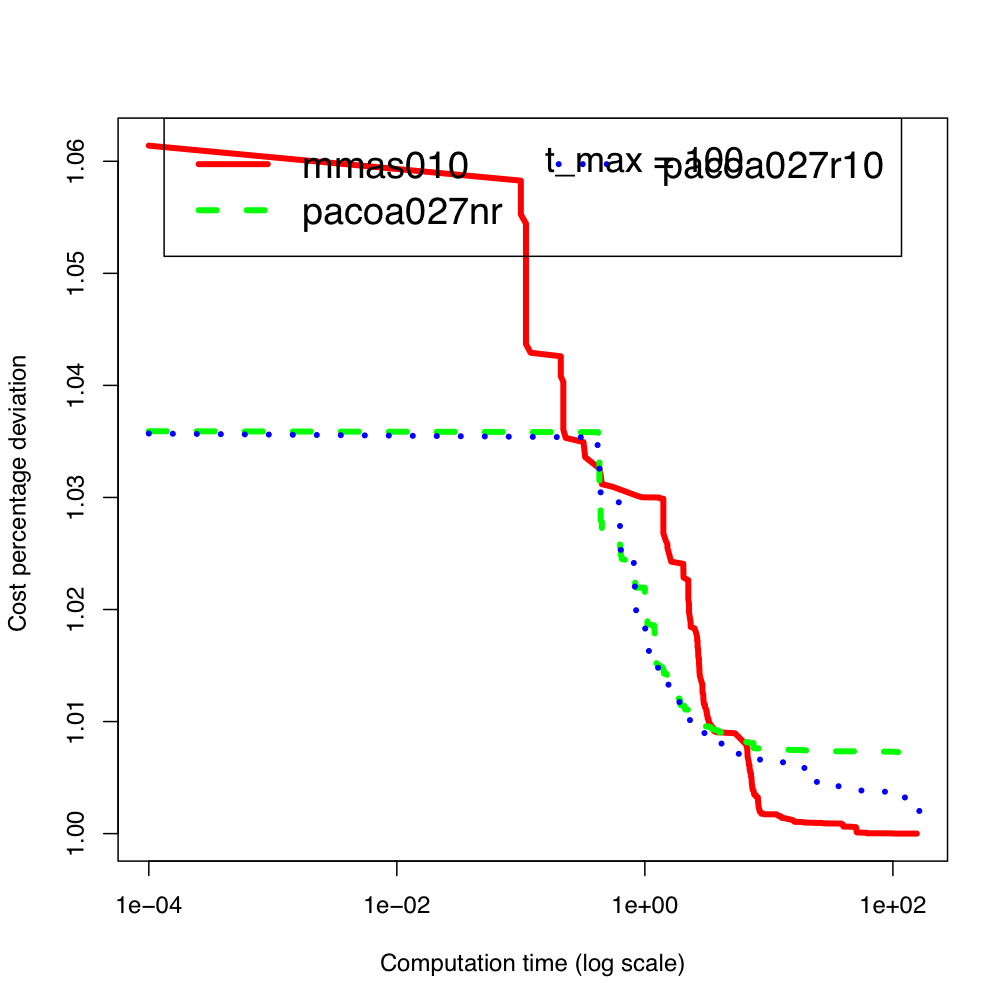 tai100b
tai100b